This exercise is Difficult. Start early!
This exercise has been allocated a long time.
There will be no extensions!
In this exercise you are required to implement a user-level thread library with a basic Round-Robin (RR) scheduling algorithm. The package should be delivered in the form of a static library. The public interface of the library is ~os/lib/uthreads.hh. You should include this header file from its original location, and implement all the functions, as explained below. You will probably find it necessary to implement internal functions and data structures. These are not visible outside the library, as they are the private part of your implementation. Therefore, you are not restricted in their number, signatures, or content.
At any given time during the running of the user's program, each of the threads in the program is in one of the states shown in the following state diagram. Transitions from state to state occur as a result of calling one of the library functions, or from elapsing of time, as explained below. This state diagram must not be changed: do not add or remove states.
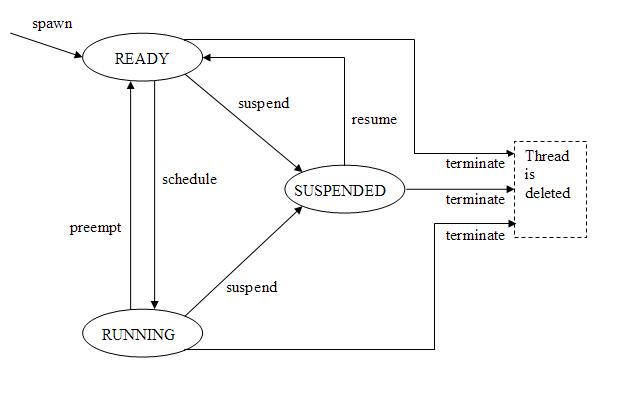
The scheduling algorithm we will use in this exercise is a simple Round Robin (RR). We ask you to read this section carefully since minor variations are possible in RR implementation, and we require the specific version that is described here.
First, note that whenever we mention time in this exercise, we mean the running time of the process also called the virtual time, and not the real time that has passed in the system. The process running time is measured by the Virtual Timer. An example of using this timer can be found here.
The round robin scheduling policy should be as follows:
int thread_init(int quantumUsecs)
Description: This function initializes the thread library.
You may assume that this function is called before any other thread library function, and that it is called exactly once.
The input to the function is the length of a quantum in micro-seconds.
Return value: On success, return 0. On failure, return -1.
int thread_spawn(void (*thread_func)(void))
Description: This function creates a new thread, whose entry
point is the function thread_func with the signature void
thread_func(void). The thread_spawn function should fail if it would cause the number of
concurrent threads to exceed the limit (MAX_THREAD_NUM). Each thread should be allocated with a stack of size STACK_SIZE bytes.
Return value: On success, return the ID of the created thread. On failure, return -1.
int thread_terminate(int tid)
Description: This function terminates the thread with
ID tid and deletes it from all relevant control structures. All the resources allocated by the library for this thread
should be released. Terminating the main thread (tid == 0) will result
in the termination of the entire process using exit(0).
Return value: The function returns 0 if the thread was successfully terminated and -1 otherwise. If a thread terminates itself or the main thread is terminated, the function does not return.
int thread_suspend(int tid)
Description: This function suspends the thread with
ID tid. The thread may be resumed later
using thread_resume. It is an error to try to suspend the main
thread (tid == 0). If a thread suspends itself, a scheduling decision
should be made. Suspending a thread in the SUSPEND state has no
effect and is not considered an error.
Return value: On success, return 0. On failure, return -1.
int thread_resume(int tid)
Description: This function resumes a suspended thread with
ID tid and moves it to the READY state.
Resuming a thread in the RUNNING or READY state has no
effect and is not considered an error.
Return value: On success, return 0. On failure, return -1.
int thread_gettid()
Description: This function returns the thread ID of the calling thread.
Return value: The ID of the calling thread.
int thread_get_total_quantums()
Description: This function returns the total number of quantums that
started since the library initialized, including the current quantum. Right
after the call to thread_init, the value should be 1. Each time a new quantum
starts, regardless of the reason, this number should be increased by 1.
Return value: The total number of quantums.
int thread_get_my_quantums()
Description: This function returns the number of quantums that were
started for the current thread, including the current quantum. On the first
time a thread runs, the function should return 1. Every additional quantum that
the thread starts should increase this value by 1.
Return value: The number of quantums of the current thread.
When a system call fails you should print a single line in the following format:
"system error: text\n"
Where text is a description of the error, and then exit(1).
When a function in the threads library fails, you should print a single line in the following format:
"thread library error: text\n"
Where text is a description
of the error, and then return the appropriate return value.
Submit tar file named ex2.tar containing:
Make sure that the tar file can be extracted and that the extracted files do compile.
This exercise is Difficult. Start early!
This exercise has been allocated a long time.
There will be no extensions!